Foundation plans are necessary for the successful execution of construction projects. After all, without a strong, solid, and durable foundation, any building will be unreliable and dangerous, not to mention that it won’t last for long, either. For foundations, it is critical to ensure that the entire structure is resistant to wind, rain, and earthquakes. This article provides an overview of foundations and the importance of foundation plans for home design, architectural planning and design services, and architecture firms.
What are foundations?
Before you learn more about foundation plans, knowing what a foundation is in the first place is a must. A foundation is the lowest portion of a structure located between the ground and the building. The primary function of a foundation is to distribute the load from the structure to the soil to endure the building’s overall weight. Most of the time, foundations are constructed using poured concrete or masonry, such as concrete blocks or brick. Masonry can resist damage from moisture and soil and boasts high compressive strength, and protect other materials as they extend above the ground. These foundations are typically reinforced with other materials like metal.
Foundations can also be constructed using treated wood posts or piers, either driven deep into the soil or rested on rock or concrete pads. Posts and piers are typically used in flood-prone areas or with buildings constructed near or on a body of water. If you don’t invest in a solid foundation plan, your property will risk expensive repairs, modifications, or foreclosure. Poor foundations have a domino effect; if they don’t act as a stable starting point, the base, support beams, and walls will soon follow suit.
RELATED: Structural engineering rates & costs for architectural design firms
What are foundation plans?
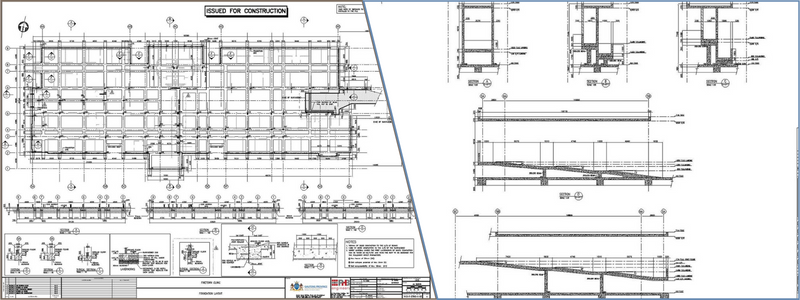
Foundation plans provide a top view of the building’s foundation walls. It is drawn by experienced architectural construction design experts according to the information in the plot, floor, and elevation plans.
A foundation plan shows:
- Locations and area
- Internal composition and dimensions
- Piers or columns, openings, beams, and girders
The building crew mainly uses foundation plans that are part of the construction documentation and plan for the foundation of the building. A structural engineer typically develops these specialized foundation plans, which involve an in-depth study of the specific materials used for the foundation and the ground under the foundation.
RELATED: How 3D modeling has impacted the architecture and design industry throughout the last 30 years
Factors that affect the foundation depth
There are various types of building foundations. Most foundations are installed at various depths except for those laid at ground level (slab-on-grade).
Several factors affect the required depth of a foundation:
- Frost depth (frost line): refers to the depth to which the ground freezes during the year’s coldest times. Frost depth is usually used to identify the minimum depth for different foundation types.
- Groundwater table: a high groundwater table can dictate which foundation type can be used and how deep the foundation can be installed. A soil study usually includes the groundwater height.
- Minimum depth: even without considering other factors, a foundation’s minimum depth is often not less than 18 inches to account for ground-level variations and topsoil removal.
- Soil bearing capacity: the soil bearing capacity determines the amount of load, force, or weight that the existing soil will be able to endure.
- Soil type: every type of soil has distinct properties that may affect its suitability to support a foundation.
RELATED: How CAD design is used in the architecture industry
Common materials used for foundations
Foundations are often constructed with either masonry, brick or concrete block, or poured concrete. Masonry materials provide high compressive strength and are more resistant to damage from soil and moisture than metal and wood materials. A masonry foundation often extends on top of the ground to protect the building materials from moisture and other risky effects of contact with the ground. Masonry foundations often have internal reinforcement using metal rebar or other materials.
Most contractors typically use hydraulic cement when sealing around raceways and pipes penetrating the concrete and masonry foundation. Some building foundations can also be constructed with piers or treated wood posts. In these cases, the foundation supports rest on concrete or rock pads or are driven deep down into the earth. Piers and posts are often used when building on or near water or flood-risk areas. The base or the sub-base of the inorganic material laid right below the foundation is among the most critical foundation materials.
Submerged clay and soil generally have limited bearing capacity and cannot withstand the loads that a building imposes. This means the soils get dug away to be replaced with a uniform, dry, dense material like crushed stone or gravel that provides maximum bearing capacity and shear resistance. Unlike soil, these base materials allow subsurface water drainage and don’t expand with high moisture levels.
RELATED: Things to consider when working with a 3D home design service
Foundation load transfer
A foundation must be designed to transfer the building load to the ground uniformly, and the loading capacity must never go beyond the soil’s bearing capacity. The foundation plans consider the projected settling from the building to ensure every movement is controlled to avert structural damage. The foundation’s overall design, ground characteristics, and superstructure are studied to determine strategies for construction.
Requirements for foundation plans
The following is a checklist of essential foundation plan features. While this list is not exhaustive, it can serve as a helpful guide:
- Dimensions and notes
- Door locations and sizes
- Drains and sump (if necessary)
- Dwarf walls
- Existing attached structures
- Exterior walls
- Fireplace location
- Footings for foundation columns, piers, and walls
- Heating appliances
- Plumbing location
- Room names and sizes
- Smoke alarm
- Window locations and sizes
- Woodstove location
A stamped, professional design must be submitted if the foundation plans are slab-on-grade or non-standard construction.
RELATED: How much blueprints cost for CAD floor plans, and 2D drawings rates at drafting firms?
Steps for creating a foundation plan
- Choose the location of the structure.
- Choose the scale for the foundation drawing.
- Find the outline of the foundation walls based on the floor plan.
- Draw the foundation piers, walls, and columns.
- Use the breaks in walls to indicate access holes, vents, windows, and doors.
- Draw the footings for the foundation walls first, then the footings for the piers and columns, and lastly, for the fireplaces and chimneys.
- Draw the supporting beam using the centerline symbol if required.
- Display the size, spacing, and direction of the floor joists or trusses.
- Add in any necessary sections and dimensions.
- Letter the required notes.
- Shade the wall drawings.
What is the difference between basement plans and foundation plans?
It is easy to confuse foundation and basement plans because both drawings follow the same procedure. Foundation plans provide essential information for those in charge of building the foundation. Basement plans include floor plan design services, foundation plans, windows, doors, stairs, built-in fixtures or appliances, and interior walls.
The bottom line
Regarding home design and architecture, plan everything from top to bottom. It is essential to consider structural elements and the room layouts to determine their respective sizes. The foundation is a critical segment of the overall house design since it is vital for supporting the entire structure. With the help of foundation plans, home design, and architecture firms will understand foundation requirements from the depth to the materials used and the load transfer. These are essential to ensure a solid foundation that will support your home for years.
How can Cad Crowd assist
Cad Crowd helps redefine the workflow in construction and architecture companies by offering a complete set of design services in one convenient location. Our broad network of professionals includes architects, freelance engineers, drafters, 3D architectural designers, and more. Our services are flexible and customizable; we can meet the demands of any project.
Hire the professional help you need when you need it! Get an estimate now.
The post Why Good Foundation Plans are Important for Home Design & Architecture Firms first appeared on Cad Crowd.